Quick Summary
How do QR codes work? This guide explains the technology behind QR codes, including their structure, data encoding, and why they’re so reliable. Learn how QR codes store information, how scanners decode them, and how Enqode QR helps you create smarter, more effective QR codes for any use case.
Table of Contents
Introduction
QR codes are everywhere—on products, ads, menus, receipts, and business cards. But have you ever wondered how do QR codes work and what makes them so fast and reliable?
This guide breaks down the technology behind QR codes, from data storage to instant scanning. Whether you're a tech enthusiast or marketer, understanding QR codes helps you use them more effectively.
What is a QR Code, Technically?
A QR code (Quick Response code) is a type of 2D barcode that stores data both horizontally and vertically. Unlike traditional barcodes, QR codes use squares and patterns to encode information efficiently.
- URLs: Instantly open websites or landing pages
- Plain text: Display messages or codes
- Contact details: Share vCards or business info
- Wi-Fi credentials: Connect to networks with a scan
- App links: Direct users to app stores
- Payment information: Enable fast, contactless payments
QR codes are popular because they’re fast to scan, easy to generate, and readable even when slightly damaged.
How Data is Stored Inside a QR Code
QR codes store information using a grid of black and white modules. Each square represents binary data—black for 1, white for 0. The more data you encode, the denser the QR code becomes.
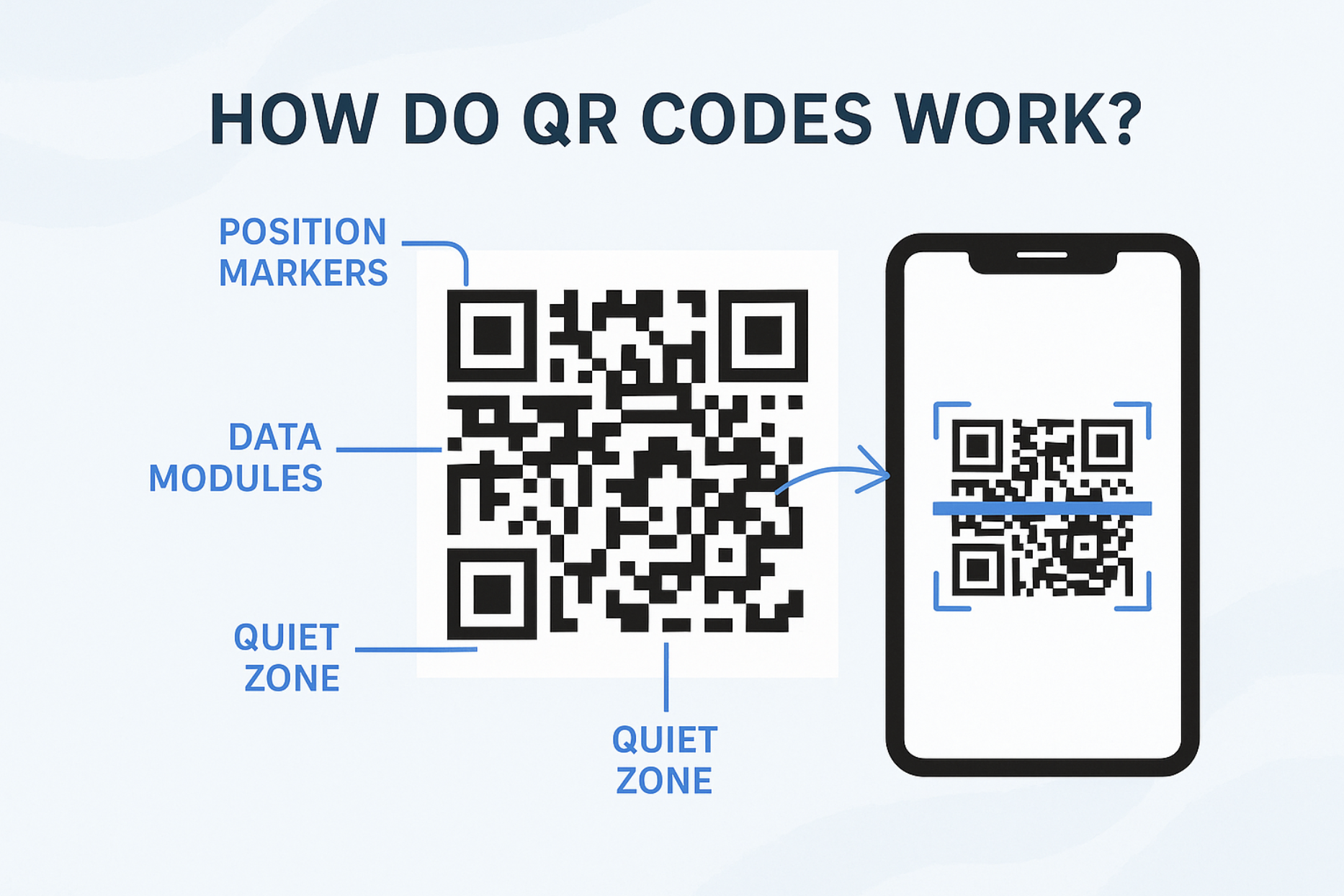
Key components of a QR code:
- Finder patterns: The three large squares in the corners help scanners quickly locate and align the code.
- Alignment patterns: Ensure readability even when the code is tilted.
- Timing patterns: Help identify rows and columns.
- Data and error correction: Encodes the actual information plus error correction to recover damaged codes.
How a QR Code Scanner Works
- Scan & Detect: Your camera detects the finder patterns and identifies the QR code.
- Decode: The app or browser reads the binary pattern (1s and 0s) and converts it into characters.
- Action Triggered: Based on the content (e.g., a URL or contact), the device prompts an action—such as opening a web page, adding a contact, or joining Wi-Fi.
QR scanners use error correction (typically Reed-Solomon) so up to 30% of the code can be damaged and still work.
Why QR Codes Are So Reliable
- Redundancy: QR codes have built-in error correction.
- High capacity: Can hold up to 4,296 alphanumeric characters.
- Fast scanning: Readable in less than a second.
- 360-degree readability: Can be scanned from any direction.
- Damage-tolerant: Still work with partial smudging, tears, or distortions.
QR Code Versions and Sizes
QR codes come in 40 versions, ranging from 21x21 to 177x177 modules. Higher versions mean more data and denser patterns. Most everyday use cases fall within version 1 to 10.
Enqode QR automatically adjusts QR code size based on your data type.
How Enqode QR Optimizes the Process
While any QR code scanner can read a code, how you generate it impacts performance:
- Cleanly structured, high-contrast codes
- Smart error correction and size balancing
- Optional dynamic QR codes for analytics & editing
- Instant previews and download options
- Branded QR customization (logos, colors, styles)
We handle the tech so you can focus on results.
Frequently Asked Questions
QR codes work by encoding data into a grid of black and white squares, which scanners read and convert into usable information. The patterns represent binary data, and built-in error correction ensures reliability even if the code is partially damaged.
QR codes use error correction and store data in two dimensions, making them readable from any angle and even when damaged. They can hold more data and are faster to scan than traditional barcodes.
Absolutely—QR codes remain essential for contactless payments, marketing, authentication, and more. Their versatility and ease of use keep them at the forefront of digital interactions.
Conclusion
Understanding how QR codes work reveals the clever technology behind their speed, reliability, and versatility. From data encoding to error correction, every detail is designed for instant, secure access.
With Enqode QR, you can create optimized, branded QR codes that perform in any scenario—whether for marketing, payments, or information sharing.