Quick Summary
Learn how to print QR codes without losing quality—get crisp, scannable results every time. This guide covers file formats, sizing, DPI, printer settings, and testing tips so your printed QR codes always work perfectly for your audience.
Table of Contents
Introduction
QR codes are powerful tools for bridging the physical and digital worlds. Whether you're adding them to business cards, marketing materials, product packaging, or signage, the primary goal is for them to be easily scannable. However, printing QR codes incorrectly can lead to blurry, distorted, or unreadable codes, rendering them useless. Ensuring your printed QR codes retain their quality is crucial for a seamless user experience and the effectiveness of your campaigns.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the best practices for printing QR codes without losing quality, covering everything from file formats and sizing to printer settings and material choices.
Choose the Right File Format
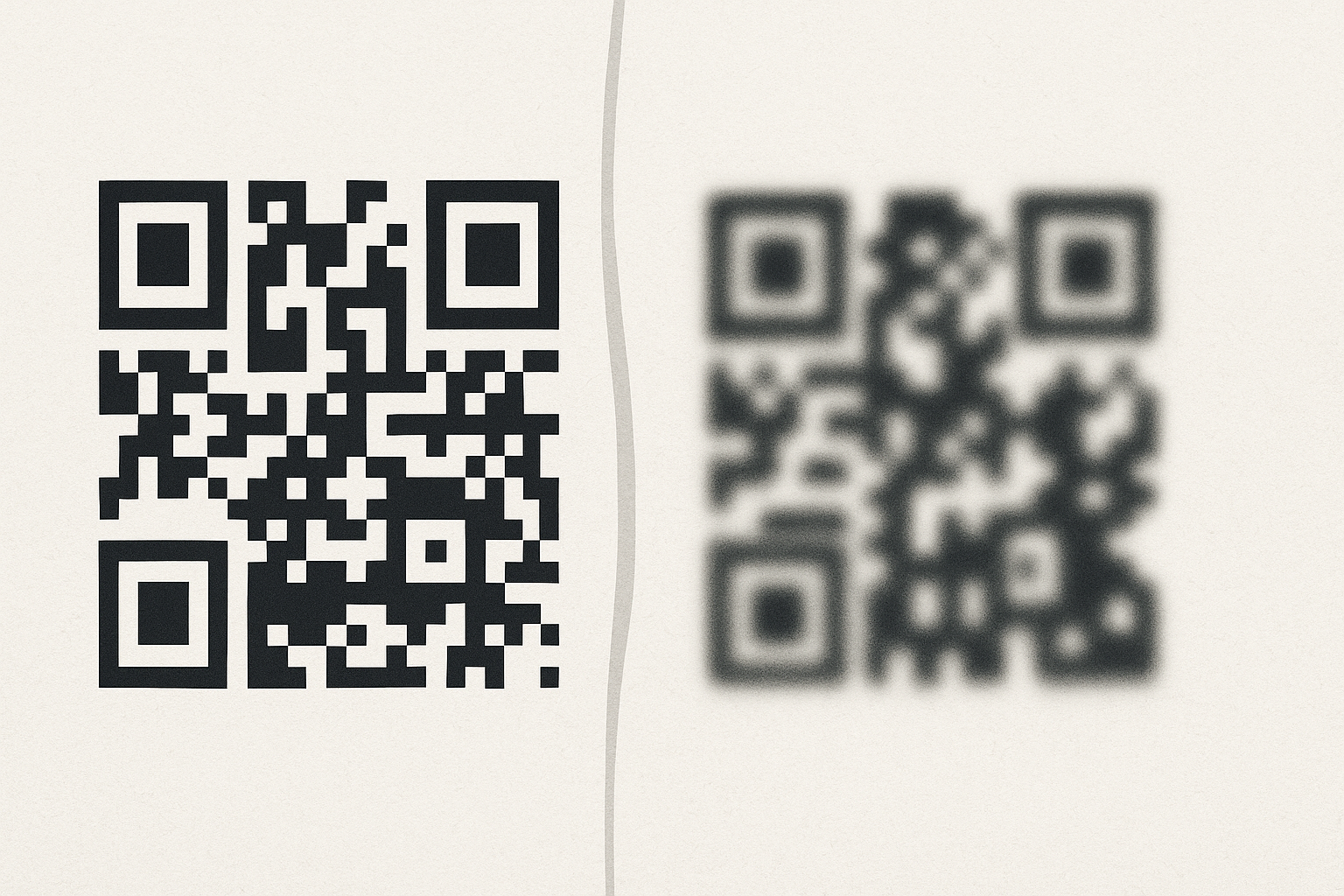
The file format you choose for your QR code artwork significantly impacts the final print quality. Vector formats are generally superior to raster formats for printing.
- Vector Formats (Recommended):
- SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics): Ideal for QR codes as they can be scaled to any size without losing sharpness or pixelating. This ensures your QR code will be crisp whether it's printed on a small business card or a large banner.
- EPS (Encapsulated PostScript): Another excellent vector format widely supported by professional printing services.
- Raster Formats (Use with Caution):
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics): A good option if saved at a high resolution (at least 300 DPI for print). PNG supports lossless compression, meaning no quality is lost when the file is saved.
- JPG/JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): Generally not recommended for printing QR codes. JPG uses lossy compression, which can introduce artifacts and blurriness, especially around the sharp edges of the QR code's modules, making it difficult to scan.
Best Practice: Always try to use SVG or EPS formats for printing QR codes whenever possible. If you must use a raster format, opt for PNG at a high DPI.
Ensure Sufficient Resolution (DPI)
Resolution, measured in Dots Per Inch (DPI), refers to the number of individual dots of ink or toner a printer lays down per inch. Higher DPI means more detail and a sharper image.
- For printed QR codes, a minimum resolution of 300 DPI is highly recommended. This ensures that the small black and white modules of the QR code are printed distinctly and without blurring into each other.
- If your QR code is intended for large-format printing (e.g., posters, banners), you might be able to use a slightly lower DPI (e.g., 150-200 DPI) as the viewing distance is greater. However, always prioritize higher DPI for optimal scannability.
Tip: When exporting your QR code from a design tool or QR code generator, ensure the DPI is set to at least 300.
Determine the Appropriate Size
The size of your printed QR code is crucial for scannability. Too small, and the modules might become too dense for a scanner to read. Too large, and it might not fit appropriately in your design or require the scanner to be too far away.
- Minimum Recommended Size: As a general guideline, aim for a minimum size of 1 x 1 inch (2.5 x 2.5 cm) for a standard QR code printed on materials like business cards or flyers.
- Consider the Content: If your QR code encodes a large amount of data, it will have more modules, potentially requiring a slightly larger print size to avoid crowding.
- Testing is Key: Always print a test version of your QR code at the intended size and scan it with various devices and scanner apps to ensure it works reliably.
- Large Format: For banners or signage viewed from a distance, the QR code will need to be significantly larger. Test scanning distances to determine the appropriate size.
Guideline: Err on the side of slightly larger rather than too small, especially if you're unsure about scanning distances or the capabilities of different scanners.
Maintain Adequate Contrast
For a QR code to be easily scannable, there needs to be a clear contrast between the dark modules (usually black) and the light background (usually white).
- Avoid Low Contrast Colors: Printing a QR code in dark gray on a light gray background, for example, can make it difficult for scanners to differentiate the modules.
- Background Considerations: Be mindful of busy or patterned backgrounds. If you must place a QR code on such a background, ensure there is a solid, light-colored area directly behind the QR code to provide sufficient contrast.
- Color Inversion: While technically possible to scan inverted QR codes (light modules on a dark background), they can sometimes be less reliably read by all scanners. It's generally best to stick to the standard dark on light.
Recommendation: Use black for the QR code modules and white (or a very light, non-reflective color) for the background whenever possible.
Select the Right Printing Material
The surface and reflectivity of your printing material can also affect QR code scannability.
- Matte Surfaces: Generally preferred as they reduce glare, which can interfere with scanning.
- Glossy Surfaces: Can cause reflections, especially under bright light, potentially making the QR code difficult to scan. If you must use a glossy material, try to position the QR code away from direct light sources.
- Texture: Avoid printing QR codes on heavily textured surfaces, as this can distort the precise edges of the modules. Smooth, flat materials are ideal.
Consideration: If using glossy materials, consider a matte varnish or laminate over the QR code area to reduce reflectivity.
Use Proper Printer Settings
The settings you choose on your printer can also impact the final QR code quality.
- Print at 100% Scale: Ensure that your printer is set to print the QR code at its actual intended size and that no scaling or resizing is applied during the printing process.
- High-Quality Print Settings: Select the highest quality print settings available on your printer to ensure the sharpest possible output.
- Black Ink/Toner: If printing in black and white, ensure your printer has sufficient black ink or toner for a dark and solid print. Low ink levels can result in faded or incomplete modules.
Advice: Perform a test print on plain paper using your intended settings before printing a large batch on your final materials.
Test Your Printed QR Codes
The most crucial step is to always test your printed QR codes with a variety of scanning devices and apps before distributing them widely.
- Use Different Smartphones: Scan the QR code with both iOS and Android devices.
- Try Different Scanner Apps: Not all scanner apps perform equally well. Test with a few different popular options.
- Test in Various Lighting Conditions: Try scanning in bright light, low light, and under artificial light.
- Test from Different Angles and Distances: Ensure the QR code is scannable from the intended viewing angles and distances.
Crucial Step: If your QR code fails to scan reliably, revisit the previous steps to identify potential issues with file format, resolution, size, contrast, material, or printer settings.
Frequently Asked Questions
SVG or EPS vector formats are best for printing QR codes at any size without losing quality. If you use PNG, make sure it's at least 300 DPI.
At least 1 x 1 inch (2.5 x 2.5 cm) for business cards or flyers. Larger codes are needed for more data or longer scanning distances.
Blurriness is usually caused by low resolution, poor file format, or printer settings. Always use high-DPI vector files and test before mass printing.
Conclusion
Printing high-quality, scannable QR codes is essential for their effectiveness. By choosing the right file format (ideally vector), ensuring sufficient resolution (at least 300 DPI), selecting an appropriate size, maintaining good contrast, considering your printing material, using proper printer settings, and rigorously testing your results, you can ensure that your QR codes work flawlessly every time, bridging the physical and digital worlds seamlessly for your audience.
Looking to generate high-quality QR codes for your printing projects? Enqode QR allows you to download your QR codes in various vector formats (SVG, EPS) ensuring they remain crisp and scannable at any print size. Explore Enqode QR's features and create perfect QR codes for all your needs.